This short tutorial presents a simple "Hello World" program for the WaveShare EX-STM8-Q48a board, either the premium version (which includes the DVK501) or the standard version with an extra RS232 board. The author used a Debian GNU/Linux system, but the tutorial should work for other Linux distributions, *BSD or other Unices.
The tools we use are
- The SDCC compiler, version 3.5.0 or later to compile C programs for the stm8.
- stm8flash, to write programs onto devices.
Hardware setup

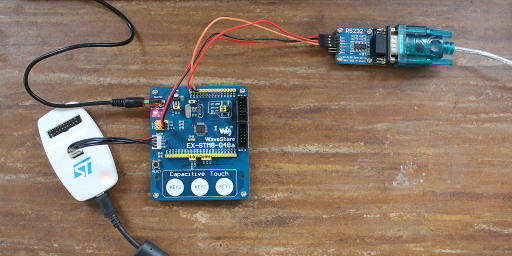
The EX-STM8-Q48a is connected to power via a USB power cable. To write our program to the board, a stlinkv2 is attached. Depending on wether we use the premium version or the standard version with RS232 board, the communication setup is different: For the EX-STM8-Q48a-105 Premium we connect the DVK501 board via the BUS-B connector, which will do for both data and power; the serial cable is then connected to the UART0 header of the DVK501. For the EX-STM8-Q48a-105 Standard with RS232 board, we connect the RS232 board to the PD5 and PD6 headers for data (TxIN to PD5, RxOUT to PD6) and to the power header for power (VCC to +5V, GND to GND); the serial cable is then attached to the RS232 board. On the other end the serial cable is attached to an RS232 port on a computer running a terminal program configured for 9600 baud, no parity, 8 bits, 1 stop bit and no flow control. We used a USB-to-serial converter and gtkterm.
Get SDCC
Depending on your operating system there might be an easy way to install SDCC 3.5.0 or newer using a package system or similar (e.g. apt-get install sdcc on Debian). While SDCC 3.4.0 should be sufficient for this tutorial, you might want to try a newer version in case you encounter any bugs. In particular, SDCC 3.4.0 has an issue with the library search path; this can be worked around by explicitly specifying the path to the standard library when linking.
SDCC binaries or a source tarball can be downloaded from its website.
Get stm8flash
The stm8flash source can be found at its GitHub location, where there is also a download link for a zip archive of the sources. To compile it, a C compiler, such as gcc, pkg-config and libusb need to be installed. Unzip the archive (e.g. using unzip stm8flash-master.zip) change into the directory stm8flash-master and type make. In case there are any errors, such as header files not found, check that pkg-config and development files for libusb are installed.
The Demo
We present a simple Demo that repeatedly outputs "Hello World!" on UART2 (the only UART the STM8S105 has). This demonstrates setting up and using the UART for serial I/O. Here is the C code:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define CLK_DIVR (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x50c6)
#define CLK_PCKENR1 (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x50c7)
#define UART2_SR (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5240)
#define UART2_DR (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5241)
#define UART2_BRR1 (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5242)
#define UART2_BRR2 (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5243)
#define UART2_CR2 (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5245)
#define UART2_CR3 (*(volatile uint8_t *)0x5246)
#define UART_CR2_TEN (1 << 3)
#define UART_CR3_STOP2 (1 << 5)
#define UART_CR3_STOP1 (1 << 4)
#define UART_SR_TXE (1 << 7)
#if __SDCC_REVISION >= 9624
int putchar(int c)
#else
void putchar(char c)
#endif
{
while(!(UART2_SR & UART_SR_TXE));
UART2_DR = c;
#if __SDCC_REVISION >= 9624
return(c);
#endif
}
void main(void)
{
unsigned long i = 0;
CLK_DIVR = 0x00; // Set the frequency to 16 MHz
CLK_PCKENR1 = 0xFF; // Enable peripherals
UART2_CR2 = UART_CR2_TEN; // Allow TX and RX
UART2_CR3 &= ~(UART_CR3_STOP1 | UART_CR3_STOP2); // 1 stop bit
UART2_BRR2 = 0x03; UART2_BRR1 = 0x68; // 9600 baud
for(;;)
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
for(i = 0; i < 147456; i++); // Sleep
}
}
SDCC is a freestanding, not a hosted implementation of C, and allows main to return void. In SDCC up to SDCC 3.6.0 putchar() used to return void. This is not standard compliant and was changed to int in current SDCC versions.
The printf() from the standard library uses putchar() for output. Since putchar() is device-specific we need to supply it. In this case we want it to output data using UART1.
The demo can be compiled simply by invoking SDCC using sdcc -mstm8 --std-c99 serial.c assuming the C code is in serial.c. The option -mstm8 selects the target port (stm8). An .ihx file with a name corresponding to the source file will be generated.
Put the demo onto the board
Assuming stm8flash and serial.ihx are in the same directory, the board is attached through an stlinkv2 device, ./stm8flash -c stlinkv2 -p stm8s105c6 -w serial.ihx will write the demo onto the board. You can see the "Hello world" by attaching a serial cable to the DB9 connector on the RS232 or DVK501 board, and using a terminal program configured for 9600 baud, no parity, 8 bits, 1 stop bit and no flow control.
More about stm8flash
stm8flash was written by Valentin Dudouyt. It works both with stlink (including the one integrated on the discovery boards) and stlinkv2 devices. The programmer can be selected using -c stlink or -c stlinkv2. The target device is selected using the -p option (to get a list of target devices, use the -p option with an option argument that is not an stm8 device, e.g. -p help. stm8flash will treat filenames ending in .ihx or .hex as Intel hex, and other filenames as binaries.
More about SDCC
SDCC was initially written by Sandeep Dutta for the MCS-51, and has a relatively conservative architecture (see Sandeep Dutta, "Anatomy of a Compiler", 2000). It has been extended by various contributors and more recently, incorporated some cutting-edge technologies, in particular in register allocation (see Philipp Klaus Krause, "Optimal Register Allocation in Polynomial Time", 2013). The stm8 backend was mostly written by Philipp Klaus Krause for his research into bytewise register allocation and spilling (see Philipp Klaus Krause, "Bytewise Register Allocation", 2015).
SDCC is a C compiler that aims to be compliant with the C standards.
Important compiler options for STM8 developers include:
-cto compile into object files to be linked later--std-c99for compilation in C99 mode (some C99 features, e.g. variable-length arrays are not yet supported in sdcc though)--opt-code-sizefor optimization for code size--max-allocs-per-nodeto select the optimization level. the default value is 3000. Higher values result in more optimized code, longer compiler runtime, and higher memory usage during compilation.